HH started in the early 1960s in Boston & London. Current studies since that time have shown better survival & quality of life for ptns on conventiona
Home
hemodialysis (HH)
Literature
review current through: Jan 2022. | This topic last updated: Feb
26, 2020.
Abbreviations:
o
BP: blood
pressure
o
CKD: chronic
kidney disease
o
Dc Np: diabetic
nephropathy
o
DOQI: Dialysis
Outcomes Quality Initiative
o
DX: Dialysis
o
Dzr: dialyzer
o
Dzt: dialysate
o
EPO: erythropoietin
o
ESA: erythropoietin-stimulating
agents
o
ESRD: end-stage
renal disease
o
FDA: US Food
and Drug Administration
o
Hct: hematocrit
o
HDX: Hemodialysis
o
HH: Home HDX
o
HT: hypertension
o
KDOQI: Kidney
Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative
o
KTx: Kidney
transplantation
o
LVH: left
ventricular hypertrophy
o
MR: Mortality
rate
o
OPD: Outpatients
department
o
PD: Peritoneal
dialysis
o
RF: renal
failure
o
RR: risk
ratio
o
RRT: renal
replacement therapy
o
Sms: symptoms
o
ttt: treatment
o
UF: ultrafiltration
o
USRDS: United
States Renal Data System.
HH started in the
early 1960s in Boston & London. Current studies since that time have shown better survival &
quality of life for ptns on
conventional, thrice weekly HH in comparison
with ptns on other DX modalities. In
regard to the cost, it has significant less costing than conventional in-center
HDX that led some authors to believe
that HH is better as compared to KTx. Despite the given benefits, the % of
prevalent DX ptns with ESRD on HH
in the US has increasingly dropped from the start of the Medicare ESRD program
in 1973 until 2002, to became 0.57 %. Similar alterations have seen in other countries. Since
2002, there has been a gradual rise in the quantity and % of all US DX ptns on HH;
by 2008, 3826 ptns (1.09
%) on HH, have been reported and along
2010 suggested that the quantity of ptns was 5000-6000 that reflecting a rising
interest in HH. Considering the USRDS 2013 data for incident 2011 ptns, total HH ptns have been rising but mainly related to
the significant rising in ptns on continuous cycler PD.
Actually, there’re several barriers to ptns choosing the home modality.
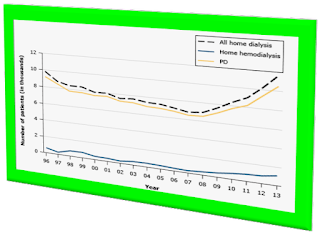
INCIDENCE/PREVALENCE
The
quantity of ptns ttt with any home DX modality (HDX
or PD) has declined along 10 ys from 1996-2008,
when the trending starts to change. By 2010, a large rise in all HH has been observed, with mostly new ptns on PD. Moreover, there was also clear rise in HH by 2011-2013, though < 1500 ptns out of about
13,000 ptns have chosen the home modality.
The entire therapy of HH still diminished.
Among incident ESRD ptns, only 9.1 % of home DX ptns were maintained on HH in 2013.
Worldwide,
there’s little or no HH, except
in few numbers of high-incomed countries
with an annual per capita national income > US $10,000, and, until recently,
the number of home DX ptns had
been mostly dropped in these areas. In 2006, there was chance for significant extension
in HH therapy in
many countries. Such extension has been observed in the US and elsewhere. A DX economic has
been developed by an international group of nephrologists observed that the
increasing home-related modalities (including PD) may help
addressing the growing DX burden all over the world. New HH programs
have been addressed in Turkey, India, China, and Hong Kong.
REASONS
FOR THE DROP IN HH
The
current lack of HH modality for ESRD therapy in the US may be attributed to:
1)
Higher
numbers of old ptns or
seriously ill, particularly those whose ESRD related to
DM or intense
vascular disease.
2)
The rapidly
rising number of out-ptns in DX units, especially for-profit units that did not
encouraging HH, although
this may be changing.
3)
The
concept that ptns should not be dialyzed without direct nurse supervision.
4)
Poor
knowledge about the advantages/disadvantages of various DX modalities
5)
Absent ptn/family
motivation, ptn fears to be sticked themselves, socially isolated, HDX techniques,
and fear of managing blood access and machines and the expected higher burden
on the family. All these can be overcome by a sympathetic staff convincing ptns
that HH is a superior type for ESRD.
6)
Absent
attention to HH,
self-care HDX, and PD by many training programs.
7)
Lacked
interest & experience with HH among most nephrologists.
8)
Little
number of proper DX programs for
ptns’ training in HH.
IMPROVED
OUTCOME
However,
HH of increasing
attention as a valuable modality
for several reasons:
1)
Realizing HH provides better outcome, better survival, better control of HT with few/no
anti-HT drugs,
better life
quality and opportunity
for re-employment, with more cost effectiveness and no adverse impacts on
fistula survival.
2)
A longer
and/or more frequently provided HDX is best given at home.
3)
A
long-term and better DX adequacy
with PD.
4)
Future concerns: Whilst
growth in ESRD incidence
in the US has been slowed along the last years, new cases grew by 3.4 % between 2005 &
2006, the 1st growing of > 3 % since 2001. However, since that time, growing
rate has flattened repeatedly, to be only 0.06 % between 2006 & 2007 and 1.2 % between 2007 &
2008. Growing of prevalence rate has been flattened along the same time period,
from 3.2 %
to -0.9 % &
0.08 %.
5)
Cost concerns: In 2008,
Medicare spent USD $26.8 billion on ESRD that
equals about 5.9
% of its entire budget. Non-Medicare ESRD = USD $12.7 billion, with a
total costing of mostly USD $39.5 billion.
6)
Shortage
of nephrologists will continue and will be compounding by the required care for
a rising number CKD ptns. Also
does the shortage of nurses.
The
studies assessing ptns’ survival on conventional HH
reported general survival rates of almost 90 & 50 % at 5 & 15 y.s, resp.. Although these reports
were proceeded by authors who’re favoring using this modality, the following data
from a report using the USRDS
database are corroborating these findings:
o
Ptns on HH had an
unadjusted lowered
mortality risk compared to ptns dialyzed as OPD (RR: 0.37 s 1.00).
o
Adjusting age,
diagnosis, comorbid diseases, and gender did not significantly alter the lowered risk of mortality in HH ptns, despite
this cohort was younger with less comorbid disease than general DX cohort (RR: risk
ratio 0.56 vs
1.00).
This improved survival, however has also been found outside
the US e.g.,
o
French
registry: improved 5- & 10-y. survival compared with DX in a
center (79 vs
59 % and 56 vs 32 %, resp).
o
Nested
case-control report: (Switzerland), 58 HH ptns matched
with an in-center HDX ptns for sex,
age, DX vintage,
and kidney disease via retrosp. analysis. 5-, 10-, & 20-y survival was greatly
higher with HH (93, 72, and 34 %, resp., vs 64, 48, and 23 %).
o
Database
analysis (Australia & New Zealand): MR risk was 50 % lower among HH ptns compared
to in-center HDX between
1996 & 2011, noting that HH ptns were younger with fewer comorbidities as
compared to in-center ptns.
Ptns
maintained on a such DX modality at
home as those who’re dialyzed in-center, the reasons of improved survival are
not well certain (except for selection bias). Blagg & Scribner alarmed the
need for DX ptns to keep their
independency avoiding the syndrome of "learned
helplessness". Ptns exerting enough responsibility and mostly know
about their disease feel "in charge"
of their own ttt achieving more favorable
outcome. Similar psychological factors may play a robust role in HH ptns. Such ptns may also be less likely to dedicate
portions or timing from their therapy, esp. those on overnight DX.
AUGMENTED
DX
Prolonged
conventional DX, thrice
weekly, is associated with improved survivals e.g., among the best ptn survival findings
in the world are those from Tassin, France showing the remarkable
benefits of thrice weekly, 8-h DX in center or at home. After 5 ys, ptns showed no
evidence of progressive nutritional deficits observed in HDX (HEMO) trial. In
Australia, many DX centers have adopted HH that’s
synonymous with extended-h.s DX due to survival, physiologic, quality-of-life,
social, and economical benefits.
More
benefits can be expected with more frequent short daily and/or long nightly HDX, both of them can be mostly easier at
home. Benefits may include more adequate DX with a higher Kt/V, better BP management
with fewer or no agents, regressed LVH
and reduced inflammatory markers, significant improvement in removing PO4 and B2 microglobulin
(esp. with nocturnal HDX), subjective improving in ptn
wellbeing both during and between sessions, better nutrition and quality of
life.
However,
considering the increased supplies, more frequent HDX
usually costs more, even if at home. So, it should be realized that overnight
nocturnal HDX 3 times a week can
provide the double as many h.s of DX/week
compared with conventional in-center HDX
as the practice in the US, less costing, and better outcome.
Long,
alternative-night HDX at home/center
is a marvelous compromise. It removes the weekly 2-day gaping between sessions
at weekends, and it has been observed that there’s a threefold raising risk for sudden
death in the 12 hs before DX after
the weekend. While it’s not as efficacious as overnight HDX 6 nights a week requiring more UF, it induces relatively better PO4 control; however, it cannot eliminate PO4 binders requirement. One report: it
can manage the biochemical agents related to bone
mineral metabolism almost like
nightly and daily short DX. Considering
costing and consumable requirements are nearly less than that with nightly and
daily HDX, extension of this regimen
should be considered.
The
2015 KDOQI guidelines: considered home long HDX 3-6 nights/week, recommending that ptns
considered for this modality should be informed about the related risks that
may include:
1)
Potential rise
in access complication(s),
2)
Higher
burden for the caregiver(s), &
3)
Rapid loss
of the residual
kidney function.
MECHANISM
OF BENEFITS
Prolonged,
thrice-weekly DX sessions and/or more
frequent HDX have variable impacts
that could be contributing to the clearly improved
outcome. One crucial difference is the ameliorated abnormal physiological cycling of body water, blood osmolality, and total body
solutes that seen with intermittent/intense conventional DX modalities. Short/long daily DX almost invariably resulting in clearer ptn
benefits compared with overnight HDX 3
times/week, and, at least with short frequent DX,
this’s not necessarily related to the higher weekly DX
dose. Despite the developed Kt/V urea has considered the common mathematical tool
to calculate the DX dose with more
frequent sessions, PO4 and
middle-molecule removal are mostly more crucial than small-molecule elimination
and augmented with increased weekly DX
dosing.
Where lab profiles
to estimate removal of B2-microglobulin
are not currently available, rather than relying on the Kt/V, the quality of DX may be
best assessed from ptn outcome and clinical Sms, e.g., effective DX therapy
may be best proved by a better quality of life that’s partially defined by lowered needs
for EPO and anti-HT drugs, better
appetite with absent fatigue and pruritus.
POSSIBLE
TECHNIQUES TO REVERSE THE DROP IN HH
Several
obstacles must be overcome to augment the % of ESRD ptns amenable for HH
modality and more frequent DX dose.
The suggested steps that nephrologists can admit to reverse the declining trend
may include:
1)
Early recognition of
potential HH ptns.
2)
Early referring to a
designated HH training
program.
3)
Early placing
of an effective A/V
fistula.
4)
Physicians/staff
must devote more
timing emphasizing
the benefits of HH: freedom,
training of techniques, independency & support, flexible schedules of DX, better
personal relationship with staff, and, particularly, better ptn survival with HH with
longer and/or more frequently provided DX.
5)
Education programs encouraging
questions/discussions and in particular targeting all ttt options
to pre-ESRD ptns.
6)
Developing
central coordination of regional HH centers to provide resources with the best specialized
training staffs (successful in British Columbia).
7)
New access modality and equipment
to augment the prescribed DX, with more frequent DX, decreasing
morbidity, and simplifying DX.
8)
Recent technology providing simple/safe
DX and for ptns
to perform, with little help from family members or others. One survey: ptns
and family may provide remote control for nocturnal HH, at least
with transition from training to HH.
9)
Recognizing: thrice weekly
HH is
significantly less costing than in-center HDX.
10) Programs for conventional HDX ptns participating
in a short, in-center, frequent DX clinical trial (2-3 weeks) to identify the benefits
of more frequent HDX.
11) Changing the reimbursement policy of Centers of Medicare/Medicaid Service paying more attention
to frequent DX. There’s
evidence that conventional HH thrice weekly and more frequent DX in particular,
either short daily or long nightly, may induce overall saving, as reduced staff timing,
less timing/frequent hospitalization, and lowered EPO/anti-HT agents needs.
Morbidity/MR from DX
is generally have declined only slightly among ptns in the US, despite the implemented
DOQI guidelines and improving Hct, serum albumin, & Kt/V values. Moreover,
the HDX (HEMO)
study declared that thrice weekly HDX,
augmenting the dose of DX above DOQI-recommended guidelines or with high-flux
membranes had no significant impact on hospitalization or ptn MR. MR still compares unfavorably with that of
Japanese, Western European, and Australian HDX
ptns.
BARRIERS
TO EXTENDED USE OF HH MODALITIES
There’re
multiple barriers to use HH modalities:
o
Absent
educated physicians, ptns, & DX staff
o
Re-imbursement
o
Ptns feelings
about staff abandonment.
It’s
possible that HH declining can be
reversed now that the barriers have been identified. HH can provide several benefits that there’s considered chance
for more DX delivery with improved
outcome. To overcome these hurdles, it’s necessary for the clinicians to take a
step with staff and ptns choosing in advance those who’re likely candidates for
one of the HH modalities.
HH MACHINES
To
continue the improvement, recent approaches/techniques have to be introduced to
provide HH delivery of more frequent modules
and more physiological DX at home. A variety
of machines dedicated for HH have
been admitted or are under evolution:
o
Aksys PHD was the 1st
machine provided specially for easily using and had FDA clearance
in 2002. It can provide ultrapure Dzt that’s ready also as replacement fluid (exempting
IV saline), and using hot
water for disinfection
to allowing Dzr &
tubing set reuse in situ for > 30 use(s) (significant decline DX supplies &
medical wastes). It has relative biocompatibility and met 2001 FDA criteria
for non-DEHP use for repetitive use,
including HDX.
o
Disadvantages may include
its large size/weight; the need for plumbing & electricity at home, with
some rise in bills; and its complexity that can be managed by company's technicians.
It’s no longer available as the Aksys Company has bankrupted in 2007.
o
NxStage System = small (only
70 pounds), more transportable machine than the older ones using 4-6 5-L bags of
ultrapure lactate Dzt integrating
onto a disposable cassette for each short daily DX, so,
increased storage space needed at home. As no need for electrical/plumbing facilities,
ptns can perform DX away from
his home without arrangement with other DX units. It’s easier for ptns to learning to use.
Larger ptns may require 5-6 bags of Dzt to get
adequate DX. Considering
the consumption of Dzt bags with
new Dzr/tubing set
for each DX session,
there’s more plastic exposure with more medical wasting.
o
The NxStage PureFlow
SL prepares > 60
L of Dzt (enough
for 3 ttt) using a
pre-packaging filtering
system that allow
ptn to prepare Dzt from tap water, avoiding
the need for Dzt bags,
except if he’s traveling.
o
The Renal Solutions Allient Sorbent HDX System was a sorbent cartridge-based system,
used at home and outside. It was also ptn friendly, only needs an electrical port
with 6 L. of drinking water for ttt. Water can be mixed with small packages of dry chemicals to be converted
to Dzt via the
sorbent cartridge, and the Dzt was permanently regenerated & recirculated.
Overnight ttt was amenable
as the sorbent cartridge was designed for 3-8-h. sessions. Renal Solutions was purchased by Fresenius
in 2007, it’s anticipated to be adapted with the sorbent technology in Fresenius
machines.
Every
system is usually focusing on the introduction of several program schemes to induce
easier/safer procedure, including:
1)
Better
computer monitoring,
2)
Better sterilization
technique, &
3)
The feedback
designing.
Other
areas of interest are related to wearable
artificial kidney and the implantable artificial kidneys. The 1st
is developed by some small companies, and at least one of them is undergoing
clinical assessment. The biggest inquiry with the wearable device is blood access, and so 2 groups are designing
wearable PD
devices.
The
evolution of an implantable artificial kidney based on the University
of Michigan Renal Assist
Device has been admitted for many
years. It’s not expected to be exposed for clinical testing for several years. Finally,
it’s important to highlight that PD is also a variety of home ttt that may play a wider role in the future.
APPROACH
Every member
in the DX team must
become advocated for HH and for
more frequent DX if it became
feasible. Until that time, conventional overnight thrice weekly or alternate-night HDX, either
at home or in a center, is suggested to be an optimal ttt schedule.
By the end of the year 2007, 841 ptns were on conventional HH thrice
weekly, 302 on alternate nights, 2396 on short daily, and 225 were on HH 5-6
nights per week.
Despite
the difficulty to receive potential ESRD
ptns early in the course of RF,
nephrologists must stress upon their colleagues that ptns on stage 3 & 4 CKD should be referred as early to teach them how
to manage their disease and to inform them about the benefits of HH, more frequent HDX,
PD, and Tx.
This
information may help reducing ptn fear and depression. It will also make it
possible for ESRD ptns to manage their illness more realistic and
provide them the opportunity to select the best module of DX ttt.
The website, Home
hemodialysis Central, is a marvelous resource for ptns
interested in home DX.
Trials
that reported better ptn outcome with HH
and more frequent HDX highlight the vitality of ptns information about various
modalities of HDX feasible to them and, in particular, the benefit (s)
of HH and more frequent HDX. Clinicians in the US & Canada believe
that home DX
therapy is underused and that 11-14
% of all HDX
ptns are candidate for ttt by HH.
A 2007 survey of 6595 delegates at 5 international HDX & nephrology conferences (57 % physicians &
28 % nurses) found that they’re mostly considering frequent
home or self-care HDX
the best long-term modality. Furthermore, at least 2 informal polls of
nephrologists asked what ttt they
would prefer, if Tx was not feasible,
found the vast majority would prefer HH,
whether they had home DX ptns or not.
So, nephrologists
and the entire DX staff
should not let their emotions or economic requirements deciding the DX modality if
there’s any chance of the ptn choosing HH. This modality of ttt is still
the best option
for many cohorts of ptns than already had the opportunity for it.


















COMMENTS