Pancreas-kidney Tx combination is now stabilized therapy for selected diabetics with ESRD. Pancreas Tx is performed as SPK transplants (most commonly
Pancreas-kidney
transplantation in DM: Surgical insights & immunosuppression
Abbreviations:
o
AB: Antibody.
o
Alm: Alemtuzumab.
o
Aza: azathioprine
o
CNI: calcineurin inhibitors
o
CyA: Cyclosporine.
o
EC-MPS: enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium.
o
ESRD: end-stage renal disease.
o
GC: Glucocorticoids.
o
IL2:
interleukin-2
o
IM/M: Immunosuppression.
o
IVC: inferior vena cava.
o
MMF: mycophenolate mofetil.
o
PAK: pancreas after kidney.
o
Prd: Prednisone.
o
PTAs: pancreas transplants alone.
o
rATG: rabbit Antithymocyte
globulin.
o
SPK: simultaneous pancreas-kidney.
o
Tac:
Tacrolimus
o
TR: Transplant recipients
o
Tx: Transplant.
o
TG: Thymoglobulin.
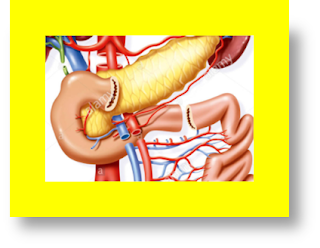
Pancreas-kidney Tx
combination is now stabilized therapy for selected diabetics with ESRD. Pancreas Tx
is performed as SPK transplants (most
commonly applied), sequential PAK Tx,
or pancreas transplants alone (PTAs).
In the US, the most commonly applied
technique for SPK Tx is consisting of
placing both organs intra-peritoneal via a vertical
midline surgical incision. Transplant centers may differ regarding
to either contralateral or ipsilateral
placement of these organs as well as the surgical therapeutic approach of the exocrine pancreas secretory
& the venous outflow. Pancreas Tx are mostly
placed on the Rt.
side & performed via enteric exocrine
drainage (≥ 90 %) & systemic venous drainage (i.e., from the graft portal vein either to the Rt
iliac vein or distal IVC).
 |
IM/M IS usually consisting
of induction
+ maintenance
therapy. Ptns receiving either an SPK or PAK
Tx, we recommend induction therapy consisting of an AB + standard triple im/m.
therapy. In TR of an SPK or PAK Tx, we suggest providing T
cell-depleting medication (either rATG-Thymoglobulin
or Alm) rather than a non-depleting IL-2
receptor antagonist:
o
If rATG
is given, we start intraoperative IV rATG-Thymoglobulin as 1-1.5 mg/kg. The
intraoperative starting dosing of rATG
is followed by 1.5- 2 mg/kg
of rATG /d. for the next 2-3 days reaching a total cumulative induction dose of 4.5-6 mg/kg. rATG
is given if, at presentation, the WBCs is > 2000/microL
& the platelet count is > 75,000/
microL. If rATG cannot be given,
we give Alm.
o
Alm is given as
single IV or SQ dose of 30 mg at the timing
of Tx.
In ptns receiving either an SPK Tx, we give
a maintenance im/m protocol that consists
of triple im/m therapy with a CNI +
antimetabolite + tapering GC:
o
With CNI,
we suggest Tac rather than CyA.
o
For antimetabolites, we suggest MMF (MMF or EC-MPS)
rather than Aza.
o Majority of ptns can start GC, oral Prd tapered to 5 mg/d by 1-2 mo after Tx.
At timing of pancreas Tx, most TR of a PAK Tx are maintained on im/m
to guard against rejection of the kidney allograft. If the ptn is already on a
triple im/m protocol that consists of
Tac + MMF or EC-MPS
+ Prd, we should not modify the maintenance plan if kidney graft
function is stabilized and the ptn is tolerating the maintenance protocol with
no or little significant untoward effects. However, considering the observed high immunogenicity
of the Tx pancreas, many ptns may necessitate
some modification of their maintenance protocol that augmenting im/m after pancreas Tx.













COMMENTS