Amyloidosis is a collection of disorders that are characterized by extracellular deposition of amyloid fibrils.
RENAL AMYLOIDOSIS
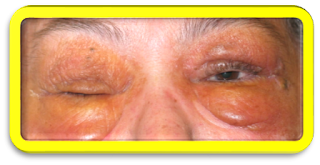
Waxy appearance of intradermal amyloid deposition around the eye
Amyloidosis is a collection of disorders that
are characterized by extracellular deposition of amyloid
fibrils. Kidney affection observed in AL
amyloidosis, characterized by deposition of Ig light chain, or AA (secondary)
amyloidosis, characterized by deposition of amyloid A. Renal affection is also the dominant
clinical picture in some hereditary forms of
the amyloid disorders.
Clinical presentation of kidney disease is variable
according to the location & magnitude
of involvement. The most common presentation of AL
& AA amyloidosis is heavy proteinuria
that is commonly associate the glomerular
deposits. Ptns with vascular disease often show:
slowly progressive CKD with
little or No proteinuria.
Less commonly, ptns with tubular deposits usually
show tubular dysfunction e.g. type 1 (distal)
renal tubular acidosis or polyuria due to nephrogenic
diabetes insipidus, and in rarely, Fanconi
syndrome. Crescentic GN is very rare.
Etiology of renal
amyloidosis relied on its type.
An abnormal clonal proliferation of plasma cells > AL
amyloidosis. Chronic inflammatory disorders > AA
amyloidosis. Adult & juvenile idiopathic rheumatoid
arthritis is the main cause of AA amyloidosis. Other major disorders
seen with AA amyloidosis include ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, chronic
pyogenic infection, inflammatory bowel syndrome, and cystic fibrosis, malignancies
& Familial Mediterranean fever. Less common conditions, genetic aberration
observed with chronic inflammation may induce AA
amyloidosis.
Ttt according to
the type of amyloidosis. Ttt of AL amyloidosis is directed at clearance of the monoclonal protein
& plasma cell clone that > reversal of organ failure. Factors influencing the renal response to
ttt include the magnitude of baseline
proteinuria & SCr. Ptns progressing
to ESRD can
be ttt with either DX or KTx. HDX
& CAPD
seem to be equally efficacious.
Prognosis for those requiring
DX is not optimistic, despite somehow better for ptns with AA
in comparison to AL amyloidosis.
Expert opinions with KTx is mainly confined
to AA & AL
amyloidosis. Limited data suggesting graft
survival is similar but ptn survival is lowered in AA amyloid disease as compared to other types of
kidney disease. Recurrence of amyloid deposits in the allograft seen in 20-33 % of cases due to persistent activity
of the underlying disease, but graft loss due to recurrent disease is NOT common. KTx is reasonable in selected AL
amyloidosis ptns.












COMMENTS