Q. 601. Describe the various component of dialysate fliud?
HEMODIALYSIS
Q. 601. Describe the various component of dialysate fliud?
A. Reference: Dugridas, hand book of dialysis 1994:
|
Dzt component: |
Conc.: |
||||
|
|
Sodium: |
|
135-155 meq/L |
||
|
|
Potassium: |
-
0 - 4
meq/L |
|||
|
|
Calcium: |
-
1.25 (std)
to 1.75 mmol/L 2.5 (std) to 3.5 meq/L |
|||
|
|
Magnesium: |
-
0
- 0.75 mmol/L 0- 1.5 meq/L |
|||
|
|
Chloride: |
-
87- 120
meq/L |
|||
|
|
Bicarbonate: (standard) |
-
25-40 meq/L |
|||
|
|
Glucose: |
-
0 (std) to 20 mg/dl |
|||
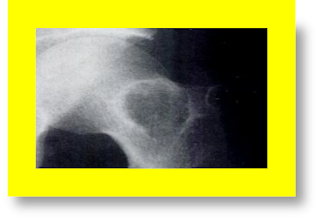
Q. 602. What are the criteria of amyloid cyst? ……
A.“Amyloid cyst”:
Œ é10 mm. (one cm) size é shoulder & hip.
é size by 30 % yearly.
Ž Joint space Normal (dcr. in osteoarthritic
cyst.).
Involve more than two joints.
Multiple (to D.D. fr. Brown tumor
of O.F.C., which’s solitary
é hip, jaw,& rib.).
-Brown tumor: A fibrous degeneration, cyst
formation, and the presence of fibrous nodules in bone, usually due to HYPERPARATHYROIDISM.
Q.603. How to prevent/ttt. amyloid cyst formation?
A. Prevention
of amyloid cyst ] use a biocompatible “Polysulphone” Dzr.
- Definitive ttt. ] R.Tx. 👈
Q.604. What is the
effect of acidosis on serum K+ level?
A. Every {0.1} P.H. Lower ] 🠞{ 0.7} mmol K+ higher. ♠
Q.605. Can dialysis patients use Sildenafil (Viagra)? 💘
- Phosphodiasterase
inhibitor, Sildenafil
(Viagra) cn be used é CrCl <30 mL/ min. é starting dose of 25 mg.
- Viagra shd NOT be given in three situation: 👌
1) Nitrate therapy.
2) Angina pectoris.
3) Recent M.I. (+ve troponin
I).
Q.606.
What tumor markers valid in
ESRD? What tumor markers false + ve in ESRD ? What tumor
markers false +ve in ESRD?
A. Tumor markers (valid)
in ESRD:
1) a.feto protein.
2) Total PSA.
3) C.A. 72
4) C.A. 125 in
non-P.D. ptn.
_ Tumor markers
false +ve in ESRD?
A.False +ve markers: ✋
1. C. A.
2. G.G.T.
3. C.A. 125. (in P.D.).
4. Acidic P.S.A.
5. C.E.F.
- AST/ALT 🠞 Normal or low in
ESRD.
Q. 607. What are the types of immunoadsorption?
R Protein A
coated.
‚ Phenyl alanine
coated.
ƒ Anti-human A.B. coated.
Q.608. What are the
indications of plasmapharesis (Pph)?
A. Indications of Pph:
I. Standard Pph:
1) Anti-GBM.(Goodpasture's
syndrome).
2) TTP/
HUS.
3) Mixed
cryog. with or without
polyneuropathy.
4) Hyperviscosity syndrome. (waldenstrom).
II.
Supportive Pph:
1.
RBGN (crescentic G.N.).
2.
Myeloma
kidney.
3.
Post-transfusion
purpura.
4.
Sickle
cell disease. (Cytapharesis).
5.
Familial
hypercholesterolemia.
III. OTHERS:
i. Recent FSGS. (post Tx).
ii. A.B.- mediated rejection.
iii. Recent HLA sensitization.
iv. Recurrent N.S.
v. IgA: short term benefit.
vi. Lupus cerebritis.
vii. ANCA- associated Vasculitis.
viii. Thrombocytosis.
ix. i.x. Guian Barre Snd.
x. |M. Gravis.
Q.609. In which situations plasmapharesisis is NOT beneficial?
A. Pph is NOT beneficial é: 👌
ΠC.A.N.
Amyloidosis.
Ž Lupus
Nephritis.
Q. 610. Describe the
technique of plasmapharesis (Pph)?
A. Technique of Pph:
I. Filter⮚ Membrane- plasma
filter, e.g. cryofilter.
II. Separator⮚ Centrifugal cell separator.
Q. 611. What are the side effects of plasmapharesis (Pph)?
A. “Side effects”of Pph: ⮚
Infection.
‚ Access clotting.
ƒ Bleeding tendency.
„ Thrombocytopenia.













COMMENTS